ADB commands provide access to a Unix Shell that runs a command directly on your Android device. An ‘adb shell’ command in a terminal sends a signal to your device and triggers the remote shell command console. Thus ADB Shell commands let you control your Android device. In this article, we’ve compiled a huge list of ADB Shell commands using which you can perform amazing tasks like managing apps and files, debugging your device, enabling and disabling features, and tweaking it to get the most out of it.
Please note that there are 2 prerequisites before you can utilize ADB and Fastboot commands.
- Android SDK Platform-tools for Windows, macOS, or Linux
- Enable and authorize USB Debugging on the Android device
List of ADB Shell Commands with Examples
In this ADB Shell commands cheat sheet, I’ll try to explain the function of all commands with examples.
adb shell
This command activates the remote shell command console on the connected Android smartphone or tablet. 
Before you can execute an ADB Shell command, you’ll need to type ‘adb shell‘ in the command window, press Enter, and type or paste the rest after the ‘$‘ sign.
adb shell pm uninstall
Using this command followed by the app package name, you can easily uninstall unwanted system apps.
adb shell pm uninstall -k --user 0 com.facebook.appmanager
-k: Keep the app data and cache after package removal. If you want the app data to be cleared as well, use the following
adb shell pm uninstall --user 0 com.android.chrome
If you don’t know the app package name for the apps to remove, use adb shell pm list packages to find it.
This command can help you if you want to remove bloatware from your Android phone. Please note that most system apps don’t have the ‘Uninstall‘ option on the device but this command works magically.
adb shell cmd package install-existing
Using the above command, you can re-install an uninstalled system app.
adb shell cmd package install-existing com.facebook.appmanager
adb shell pm disable-user <package-name>
If you want to disable a system app on your Android device, you can execute the above command followed by the app package name
adb shell pm disable-user --user 0 com.google.ar.core
adb shell pm clear <package-name>
Using this command, you can delete all data associated with an app.
adb shell pm clear --user 0 com.facebook.appmanager
adb shell pm hide <package-name>
If you want to hide an installed app on your Android device, you can execute this command line followed by the app package name.
adb shell pm hide --user 0 com.whatsapp
adb shell pm list packages
Using the above ADB Shell command, you can print the list of the app package names for all apps installed on your Android device. You can use this command with different parameters to get a more specific list of app packages.
For instance, if you want to list the system apps only, use
adb shell pm list packages -s
The following command will print the list of all installed packages with the path of the APKs.
adb shell list packages -r
To list all third-party apps installed on your Android phone or tablet, you issue the following command.
adb shell pm list packages -3
Do you want ADB Shell to show the list of all enabled or disabled apps on your device, try the command with parameters like ‘-d‘ (for disabled apps), ‘-e‘ (for enabled apps), and ‘-u‘ (for uninstalled apps).
adb shell pm list packages -d
adb shell pm list packages -e
adb shell pm list packages -u
The following command will list the app packages with their installers.
adb shell pm list packages -i
To list app packages with specific keyword filters.
adb shell pm list packages <keywords>
To find the list of apps along with their associated packages, execute the following command
adb shell pm list packages -f
You can easily get a list of group packages by a certain manufacturer, or some common term. For instance, if you want to list all apps by Google, you can use the following command.
adb shell pm list packages | grep 'google'
You can replace ‘google’ with ‘samsung’, ‘huawei’, ‘xiaomi’, ‘miui’, ‘evenwell’, ‘android’, ‘facebook’, etc. to get the desired list of packages.
Don’t Miss: ADB Command to Improve Performance on Android
adb shell pm path <package-name>
This command displays the APK path on the device’s file system.
adb shell pm create-user
With this command. you can create a new user on your Android device.
adb shell pm create-user username
adb shell pm remove-user
Just in case you want to remove a user from your device, you can use the above command followed by the user_id as shown below.
adb shell pm remove-user user 1
adb shell pm get-max-users
With this command, you can print the maximum number of users supported on an Android device.
adb shell pm list features
Use the above command to print all supported features of the system.
adb shell pm list permissions
This command prints the list of all known permissions on the connected Android device, optionally only those in group. You can use it with the following parameters.
-g: Organize permissions by group-f: Print all information-s: Summary of permissions-d: List dangerous permissions only-u: List the permissions seen by users only
Examples:
adb shell pm list permissions -d group
adb shell pm list permissions -d -g
adb shell pm path
Get the path of a given app package.
adb shell pm path <package-name>
adb shell settings
You can use this command to print information about specific settings on your Android device. By adding different parameters, you can find the Android settings provider, current system volume level, notification sound, device ID, Bluetooth MAC address, mobile data status, current Wi-Fi status, etc.
-
adb shell settings list system
-
adb shell settings get system volume_system
-
adb shell settings get system notification_sound
-
adb shell settings list secure
-
adb shell settings get secure android_id
-
adb shell settings get secure bluetooth_address
-
adb shell settings list global
-
adb shell settings get global mobile_data
-
adb shell settings get global wifi_on
adb shell dumpsys
It’s a very flexible command that can be used standalone or with various parameters to get data related to battery, display, CPU, RAM, storage, etc. The execution of this command will give you detailed information about the Android device’s software and hardware configuration.
Note: To use this tool, don’t forget to add permission to your Android manifest automatically android.permission.DUMP
adb shell dumpsys
Other variations of the command are as follows:
-
adb shell dumpsys package packages (get info about all installed apps)
-
adb shell dumpsys input
-
adb shell dumpsys display (get details about the display)
-
adb shell dumpsys battery (get detailed info about your device's battery and status)
-
adb shell dumpsys batterystats (battery usage statistics)
-
adb shell dumpsys activity (get a complete list of all ongoing activities on your device)
-
adb shell dumpsys cpuinfo (get detailed about CPU usage)
Executing the adb shell dumpsys cpuinfo command, for instance, will print a list of CPU usage by the running processes and apps on your Android device.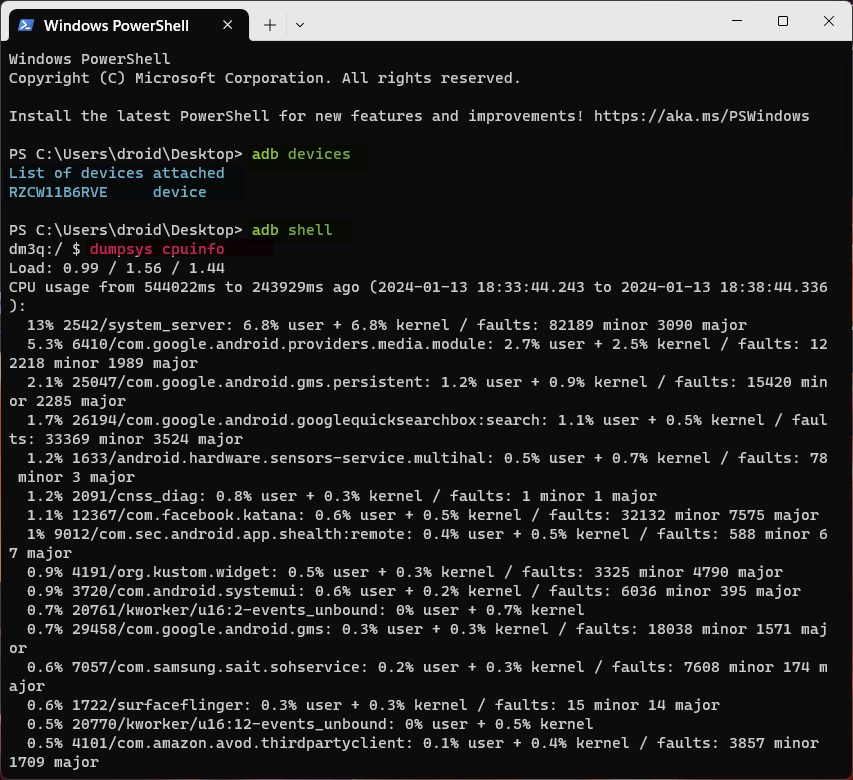
adb shell wm density
The above command can be used to find out the pixel density of your Android device’s display.
adb shell dumpsys window displays
The above command will print detailed info like pixel resolution, FPS, and DPI of your phone’s display.
adb shell wm size
You can find out the display resolution of your phone with this command.
PS C:\Users\Technastic\Desktop> adb shell wm size Physical size: 1440x3040 Override size: 1080x2280
If you want to modify the screen resolution and the pixel density of your Android device’s display. If you’re unsure about your device’s display resolution, execute the command given below. Suppose your phone’s display resolution is QHD+, you can easily change it to Full HD+ or HD+.
- FHD
adb shell wm size 1080x2220
adb shell wm density 420
- HD
adb shell wm size 720x1560
adb shell wm density 360
adb shell screencap
This command captures a screenshot and downloads it to your computer using the ‘adb pull’ command as described above.
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screenshot-01.png
adb shell screenrecord
ADB also lets you record your phone or tablet’s screen and download the recorded video to your computer. Besides, you can also set conditions like video duration, resolution in pixels, video bitrate, etc.
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
adb pull screenrecord /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
You can stop screen recording using Ctrl+C. If you want to record the screen in a specific resolution, the following command lets you set custom width and height in pixels.
adb shell screenrecord --size 1920x1080 /sdcard/screenrecord-01.mp4
Android’s screen recorder’s duration is set to 180 seconds (3 minutes) by default. You can decrease this time limit according to your needs (180 seconds is the maximum limit).
adb shell screenrecord --time-limit 120 /sdcard/screenrecord-01.mp4
Similarly, you can also determine the bitrate of the video output. To set the bitrate to 4MBPS, for example, you can use the following value:
adb shell screenrecord --bit-rate 6000000 /sdcard/screenrecord-01.mp4
adb shell getprop & adb shell setprop
The ‘getprop‘ and ‘setprop‘ commands can be used to view and set or change the configuration of the ‘build.prop’ file on Android devices. The following command, for example, displays the Android system information.
adb shell getprop
Below are some more examples:
getprop ro.build.version.sdk
getprop ro.chipname
In case you want to change the value of an entry in the build.prop, you can use the adb shell setprop commands. See the examples below:
getprop net.dns1 1.2.3.4
setprop net.dns1 1.3.4.5
getprop net.dns2 1.1.2.3
setprop net.dns2 1.2.3.4
In the same way, if you want to change the configuration of the VMHeap size on your Android device, you can use the following command.
setprop dalvik.vm.heapsize 60m
The adb shell getprop commands fetch information about Android system properties, SDK API level, Android security patch version, Soc, Android version, device model, device manufacturer, ADB serial number, OEM unlock status, Android device build fingerprint, Wi-Fi MAC address, etc.
-
adb shell getprop
-
adb shell getprop ro.build.version.sdk
-
adb shell getprop ro.build.version.security_patch
-
adb shell getprop ro.board.platform
-
adb shell getprop ro.build.version.release
-
adb shell getprop ro.vendor.product.model
-
adb shell getprop ro.product.manufacturer
-
adb shell getprop ro.serialno
-
adb shell getprop ro.oem_unlock_supported
-
adb shell getprop ro.bootimage.build.fingerprint
-
adb shell getprop ro.boot.wifimacaddr
adb -s shell getprop
To check the full configuration, running services, and information about your Android phone or tablet, use this command. First off, run the adb devices command and copy the alpha-numeric value of your device ID from the output.
PS C:\Users\Technastic\Desktop> adb devices
List of devices attached
RZ8M810BARJ device
Then execute the following command. Don’t forget to replace the device ID highlighted in blue with the ID of your device.
adb -s RZ8M810BARJ shell getprop
adb shell cat /proc/cpuinfo
Use the above command to get complete information about the CPU on your phone or tablet.
Manage App Permissions
ADB makes managing app permissions on Android a breeze. Below are some examples.
Reset Permissions
adb shell pm reset-permissions -p <app-package-name>
Grant Permissions
adb shell pm grant <app-package-name> <permission-name>
Revoke Permissions
adb shell pm revoke <app-package-name> <permission-name>
Get Device Properties
By running the following command, you can see the system properties.
adb shell getprop | grep -e 'model' -e 'version.sdk' -e 'manufacturer' -e 'hardware' -e 'platform' -e 'revision' -e 'serialno' -e 'product.name' -e 'brand'
adb shell cd
Change the ADB shell directory using ‘cd <directory>‘
adb shell
Then execute the following command:
cd /system
adb shell rm
This command lets you easily delete a file or folder from your Android device’s storage. Launch the command window, execute the ‘adb shell’ command, and then try the following command with ‘-f‘ (to delete a file) and ‘-d‘ (to remove a directory) parameters.
rm -f /sdcard/com.whatsapp.apk
rm -d /sdcard/WhatsApp
Note: Instead of ‘rm-d‘, you can also use ‘rmdir‘.
adb shell mkdir
Besides deleting an existing directory or folder, ADB Shell lets you create a new directory or sub-directory. Not only that, you can set permissions for the newly created folder.
mkdir /sdcard/NewFolder mkdir -p /sdcard/NewFolder/NewFolder1 mkdir -m 644 /sdcard/NewFolder
adb shell cp
‘cp‘ stands for ‘copy and allows you to copy files and directories on your Android device.
To copy files and then paste them, mention the source and destination locations as shown below:
cp /sdcard/OPWallpaperResources.apk /sdcard/DCIM/Camera
adb shell mv
‘mv‘ stands for ‘move’. This command moves a file stored on your device from the source to a destination location.
mv /sdcard/livewallpapers.apk /system/app
The following command will allow you to move a file with a new name.
mv /sdcard/livewallpapers.apk /sdcard/Wallpapers
adb shell top
This command displays the list of top CPU processes on an Android phone or tablet. CPU processes monitor can be stopped using Ctrl + C.
adb shell ip
Find out the WiFi IP address of an Android phone or tablet.
ip -f inet addr show wlan0
adb shell netstat
Displays the network statistics of Android phones.
adb shell netstat
Get a List of Device Features
adb shell pm list features
Make a Call
Make a call using an ADB command via your computer.
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.CALL -d tel:+19797220011
Send SMS screen
If you want to send a text message using a command, try the following code.
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.SENDTO -d sms:+19797220011 --es sms_body "Test Message" --ez exit_on_sent false
You can use the following command to
Input Text in a Text Field
You can input or print text on your phone using the command. I tested this command in Messages, WhatsApp, Facebook, etc. If a messaging app is not open, the text will open in Google Search.
adb shell input text 'I love this adb command'
Open URL in a Web Browser
Open a URL in your Android phone’s default web browser.
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d https://technastic.com
Open the Gallery App
Executing the following ADB Shell command will open the Gallery app.
adb shell am start -t image/* -a android.intent.action.VIEW
ADB Shell Key Event Commands
Key Event Commands to Toggle and Trigger Functions
Android devices support KeyEvent commands that can let you perform certain actions that require you to press a hardware button or tap an app or UI option. You can control your Android phone or tablet device and even launch apps by using these KeyEvent commands. These commands might come in handy if the hardware keys on your device are unfunctional due to physical damage.
-
Turn Android device ON or OFF: adb shell input keyevent 2
-
Press App Switcher Button: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_APP_SWITCH
-
Press Home button: adb shell input keyevent 3
-
Press Back button: adb shell input keyevent 4
-
Press Call button: adb shell input keyevent 5
-
End a call: adb shell input keyevent 6
-
Press Power Button to wake up screen: adb shell input keyevent 26
-
Turn ON the camera: adb shell input keyevent 27
-
Open web browser: adb shell input keyevent 64
-
Press the Enter key: adb shell input keyevent 66
-
Press Backspace button: adb shell input keyevent 67
-
Open Contacts app: adb shell input keyevent 207
-
Decrease display brightness: adb shell input keyevent 220
-
Increase Display brightness: adb shell input keyevent 221
-
Cut text: adb shell input keyevent 277
-
Copy text: adb shell input keyevent 278
-
Paste text: adb shell input keyevent 279
-
Make the device sleep: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_SLEEP
-
Make device wakeup: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_WAKEUP
-
Toggle Power menu: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_POWER -
Trigger Volume up: adb shell input keyevent 24
-
Trigger Volume down: "adb shell input keyevent 25
-
Trigger Zoom in: adb shell input keyevent 168
-
Trigger Zoom out: adb shell input keyevent 169
-
Menu: adb shell input keyevent 82
-
Open Notifications: adb shell input keyevent 83
-
Launch Search: adb shell input keyevent 84
-
Play or pause media: adb shell input keyevent 85
-
Mute audio: adb shell input keyevent 91
-
Page up: adb shell input keyevent 92
-
Page down: adb shell input keyevent 93
-
Open Calendar: adb shell input keyevent 208
-
Launch Music: adb shell input keyevent 209
-
Open Calculator: adb shell input keyevent 210
-
Volume up: adb shell input keyevent 24
-
Make the lock screen sleep: adb shell input keyevent 223
-
Wakeup the lock screen: adb shell input keyevent 224
-
Make device wakeup: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_WAKEUP
-
Toggle Power menu: adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_POWER
Android Keyboard-related Key Event Commands
You can use the following key events commands to print letters, numbers, and symbols on your Android device right from your computer. ADB can help you wake up the device and unlock the screen PIN or pattern without touch input.
-
Clear: adb shell input keyevent 28
-
Caps lock: adb shell input keyevent 115
-
Number '0': adb shell input keyevent 7
-
Number '1': adb shell input keyevent 8
-
Number '2': adb shell input keyevent 9
-
Number '3': adb shell input keyevent 10
-
Number '4': adb shell input keyevent 11
-
Number '5': adb shell input keyevent 12
-
Number '6': adb shell input keyevent 13
-
Number '7': adb shell input keyevent 14
-
Number '8': adb shell input keyevent 15
-
Number '9': adb shell input keyevent 16
-
Letter 'a': adb shell input keyevent 29
-
Letter 'b': adb shell input keyevent 30
-
Letter 'c': adb shell input keyevent 31
-
Letter 'd': adb shell input keyevent 32
-
Letter 'e': adb shell input keyevent 33
-
Letter 'f': adb shell input keyevent 34
-
Letter 'g': adb shell input keyevent 35
-
Letter 'h': adb shell input keyevent 36
-
Letter 'i': adb shell input keyevent 37
-
Letter 'j': adb shell input keyevent 38
-
Letter 'k': adb shell input keyevent 39
-
Letter 'l': adb shell input keyevent 40
-
Letter 'm': adb shell input keyevent 41
-
Letter 'n': adb shell input keyevent 42
-
Letter 'o': adb shell input keyevent 43
-
Letter 'p': adb shell input keyevent 44
-
Letter 'q': adb shell input keyevent 45
-
Letter 'r': adb shell input keyevent 46
-
Letter 's': adb shell input keyevent 47
-
Key 't': adb shell input keyevent 48
-
Letter 'u': adb shell input keyevent 49
-
Letter 'v': adb shell input keyevent 50
-
Letter 'w': adb shell input keyevent 51
-
Letter 'x': adb shell input keyevent 52
-
Letter 'y': adb shell input keyevent 53
-
Letter 'z': adb shell input keyevent 54
-
Key 'comma': adb shell input keyevent 55
-
Key 'period': adb shell input keyevent 56
-
Key 'alt_left': adb shell input keyevent 57
-
Key 'alt_right': adb shell input keyevent 58
-
Key 'shift_left': adb shell input keyevent 59
-
Key 'shift_right': adb shell input keyevent 60
-
Key 'tab': adb shell input keyevent 61
-
Key 'space': adb shell input keyevent 62
-
Key 'symbols': adb shell input keyevent 63
-
Key 'minus': adb shell input keyevent 69
-
Key 'equals': adb shell input keyevent 70
-
Key 'left bracket': adb shell input keyevent 71
-
Key 'right bracket': adb shell input keyevent 72
-
Key 'backslash': adb shell input keyevent 73
-
Key 'semicolon': adb shell input keyevent 74
-
Key 'apostrophe': adb shell input keyevent 75
-
Key 'slash': adb shell input keyevent 76
-
Key '@': adb shell input keyevent 77
The following key events work on the numerical keypad of Android devices.
-
Number '0': adb shell input keyevent 144
-
Number '1': adb shell input keyevent 145
-
Number '2': adb shell input keyevent 146
-
Number '3': adb shell input keyevent 147
-
Number '4': adb shell input keyevent 148
-
Number '5': adb shell input keyevent 149
-
Number '6': adb shell input keyevent 150
-
Number '7': adb shell input keyevent 151
-
Number '8': adb shell input keyevent 152
-
Number '9': adb shell input keyevent 153
-
Symbol 'divide': adb shell input keyevent 154
-
Symbol 'multiply': adb shell input keyevent 155
-
Symbol 'subtract': adb shell input keyevent 156
-
Symbol 'add': adb shell input keyevent 157
-
Symbol 'dot': adb shell input keyevent 158
-
Symbol 'comma': adb shell input keyevent 159
-
Symbol 'enter': adb shell input keyevent 160
-
Symbol 'equals': adb shell input keyevent 161
Download: ADB Shell Commands List PDF
Read Next: ADB Commands for Battery Optimization on Android
Source: Google Developers