Mozilla Firefox, very much like Linux, is free and open-source software. Mozilla claims to be a non-profit company as well. If you’re wondering where I’m leading with this, it is the fact that Mozilla Firefox is the default browser for Ubuntu and some other Linux distributions. And now you know why Firefox fits so nicely into the philosophy of Linux. Philosophy aside, Firefox is but a piece of software. This means it can bug out sometimes. This may make you want to uninstall Firefox.
Whatever your reasons, uninstalling Firefox is not something difficult compared to other app uninstallations on Ubuntu. Uninstalling Firefox from a Mac or Windows is more complicated than installing it. If you uninstall Firefox or install it again, you will find the new installation still has the same settings and preferences that made things worse in the first place. This is because uninstalling Firefox the traditional way does not remove the settings and preferences. Do the following to uninstall and reinstall Firefox on Ubuntu.
Install GKSu
GKSu is a library that provides a Gtk+ frontend to su and sudo.
Removing the data stored by Firefox involves deleting files created by Firefox in the root directories. You can do this via the terminal without any need for GKSu. However, if you prefer to do things with a graphical interface, you will need to install GKSu in case you don’t already have it. To install it, enter the following in a terminal:
sudo apt install gksu
How to uninstall Firefox on Ubuntu
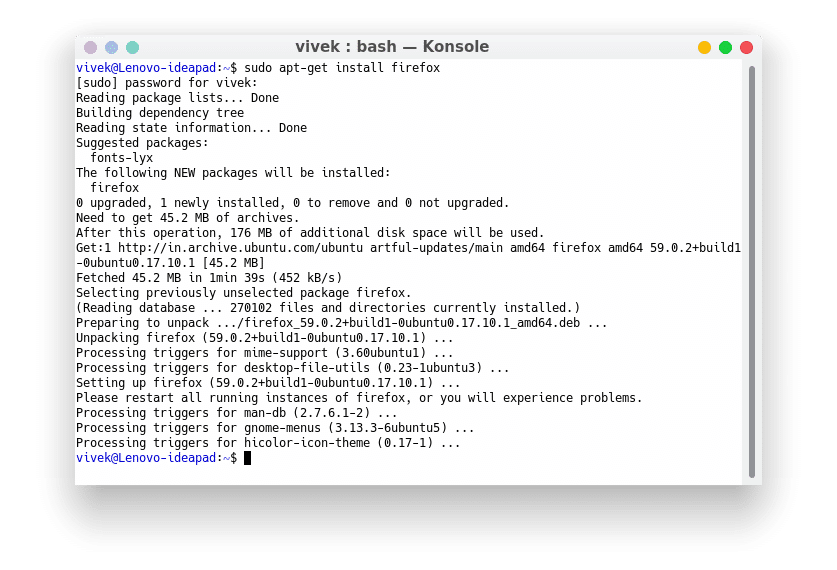
- In a terminal window, run the following command:
sudo apt-get purge firefox
- Once that is done, launch your file browser and head to the home directory. Launch it with root permissions since some of the folders that need to be removed can’t be removed without root access. This is where GKSu comes in handy. Execute the following command to launch Nautilus, the default file manager in Ubuntu, as a root app.
gksu nautilus
- Delete the folder named .mozilla if it is still there. This is a hidden folder, so you will have to make sure hidden files and folders are visible to see it. If you were having trouble with Adobe Flash Player on Firefox, you may also want to delete the folders named .macromedia and .adobe, if present. These folders generally contain the flash cookies stored by the browser.
- Now let’s remove folders in the root directories. First, delete the folder named ‘firefox’ inside etc (/etc/firefox/). This is where your preferences and user profiles are stored.
- Similarly, go to the /usr/lib/ folder and delete the folders named firefox and firefox-addons there. It’s possible that you may not find these folders there anymore.
- Reboot your computer to get rid of any temporary files.
How to install Firefox again
You can now install the same Firefox again, or install a different version, such as one of the daily builds or betas. The daily builds are unstable, and you might be frustrated even if you use Firefox as a secondary browser. So we’d rather not recommend it. Beta builds are relatively more stable and usable.
Install Firefox stable
Run this command in a terminal:
sudo apt-get install firefox
Install Firefox official beta
If you like to test the beta versions, you can install Firefox with a command and then upgrade to a beta. This requires adding the official Firefox beta PPA.
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:mozillateam/firefox-next sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
So, you know how to install and uninstall the Firefox browser on Ubuntu.