Do you need to use an ADB command on your Android phone or tablet to perform a task, but don’t have access to a computer? Earlier, it was impossible to run commands on an Android device itself without superuser permissions. Thankfully, Terminal emulator apps like aShell (Shizuku) and Termux allow you to use ADB natively. This tutorial will explore different methods to run ADB on Android devices without root, including Termux, aShell, and WebADB.
Let’s check out different methods to harness the power of ADB on Android devices without a PC.
1. Using Shizuku-supported aShell App
Shizuku acquires system APIs and permissions through wireless debugging and passes them to supported apps. Unlike other apps that require root privileges to modify Android devices, Shizuku leverages certain Android permissions. You can use the Shizuku-supported apps to do amazing things without rooting your device. Besides modifying, tweaking, and customizing your Android phone, Shizuku also makes it possible to use ADB on Android devices without root.
- Download and install Shizuku on your Android device.
- Enable the Developer options on your device.
- Open Shizuku and tap the Pairing button under the ‘Start via Wireless debugging’ section.

- Shizuku will request notification permission. To grant it, tap Notification options and allow notifications for Shizuku.

- Having allowed notifications, tap the back button on the navigation bar and select Developer options.

- Go to the Debugging section, tap Wireless Debugging, and enable the feature. Next, select the Pair device with pairing code option.

- A pop-up with a pairing code will appear, and you’ll receive a notification from Shizuku requesting to enter the 6-digit code.
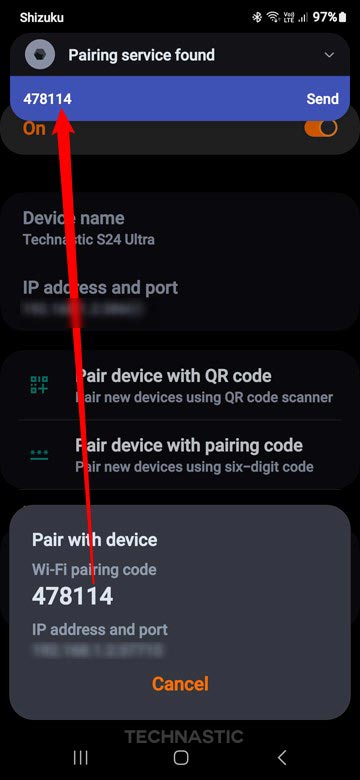
- Type the Wi-Fi pairing code and tap the Send option.
- In Shizuku, tap the Start button. The app will run a script and start the Shizuku service in the background.
- Exit Shizuku and install aShell from the Play Store (paid) or F-Droid (free).
- Launch aShell and grant it access to Shizuku.

- That’s it! You can now use the aShell command box to execute ADB and Shell commands on your device without root. For instance, to check the health of your phone’s battery, type “
dumpsys battery” and press the Send or Enter button.
2. Setting up ADB in Termux (Root)
It’s possible to install ADB and Fastboot on Android by cloning any of the 3 Gits listed below using a terminal emulator like Termux.
Now let’s see how you can install ADB and Fastboot on an Android phone or tablet.
- Download and install Termux from the Play Store.
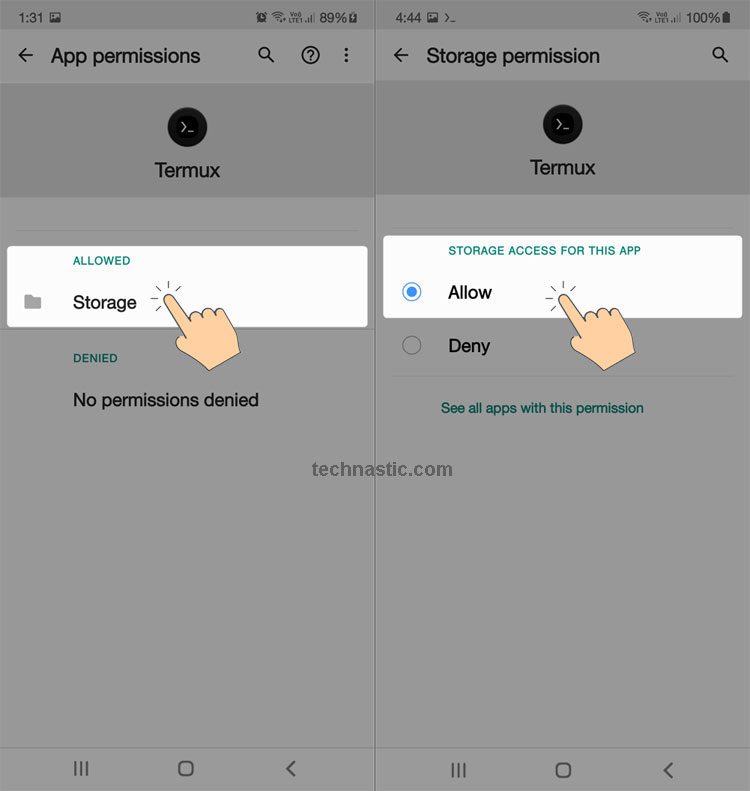
- Having installed the app, you need to grant Storage permission to Termux. To do so, go to Settings > Apps > Termux and select Permissions. Then tap Storage and select Allow.
- Now open Termux, type the following and tap the Enter key on the keyboard.
pkg update
- Now, execute the following command to upgrade Termux packages.
pkg upgrade
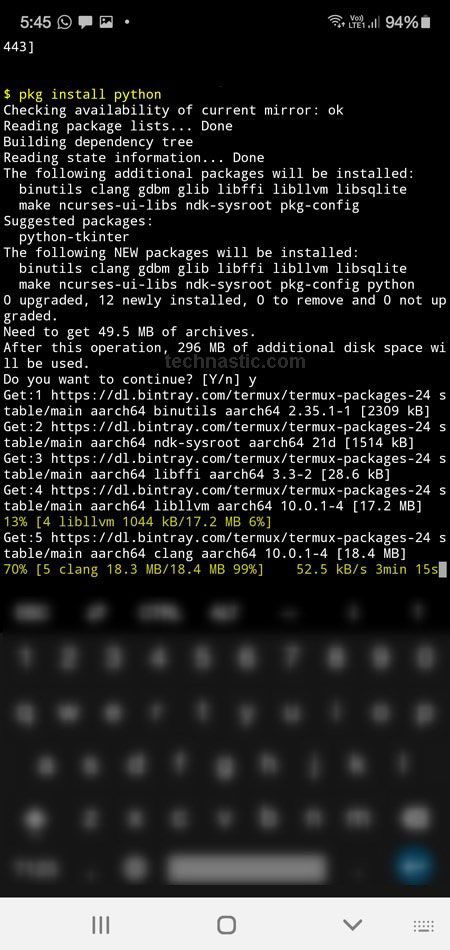
- Since ADB Fastboot Termux is a Python-based script, we must install Python on the Android device. Issue the following command in Termux.
pkg install python
- While installing Python on your Android device, you might be prompted to authorize the installation by typing ‘Y‘ (for Yes).
- Since we have to clone Git from GitHub, you’ll need to install another package called Git using this command.
pkg install git
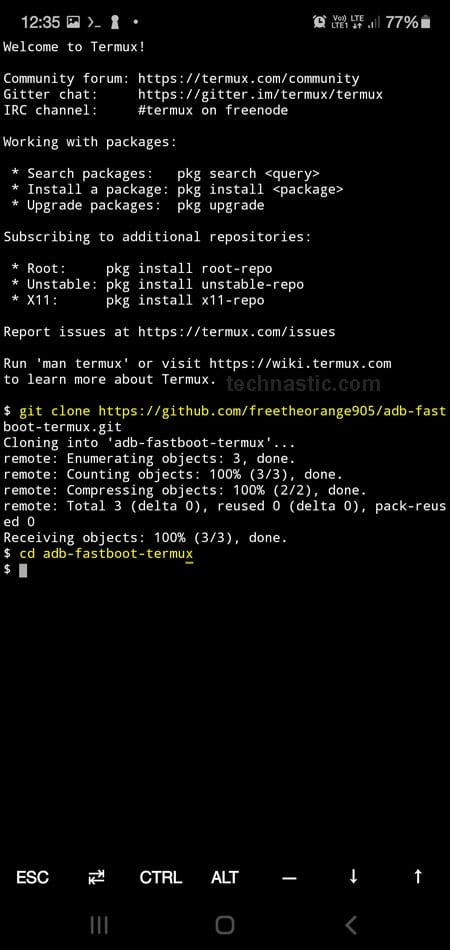
- It’s time to clone the ADB Fastboot Termux Git using Termux.
git clone https://github.com/freetheorange905/adb-fastboot-termux.git
- Now that the ADB and Fastboot Git have been cloned to your Android device, we need to change the path directory using
cdas shown below (see the screenshot above).cd adb-fastboot-termux
- Finally, execute the following command in Termux.
python af.py
- As soon as you tap the Enter key, a new screen will appear and you will be prompted to type 1 to install ADB and Fastboot on your Android device, and 2 to uninstall them. Type 1 and tap the Enter key.
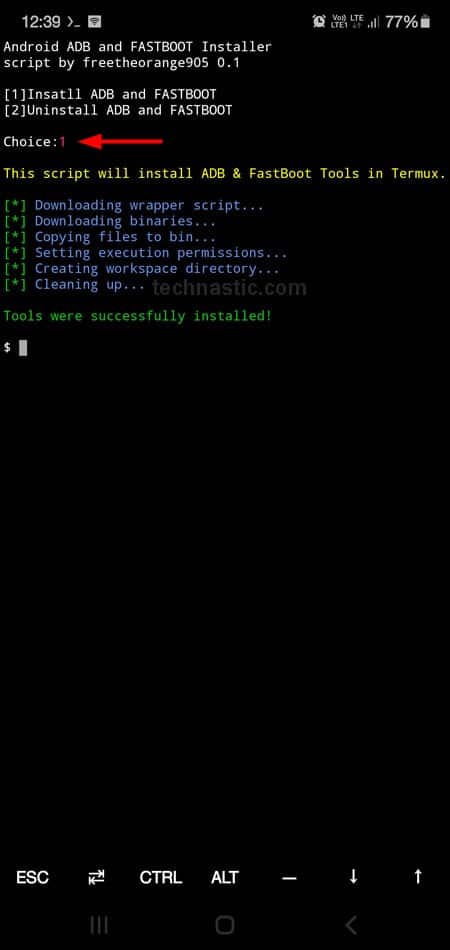
- When ADB and Fastboot are installed, you’ll get a message saying, “Tools were successfully installed!“
You can also install the ADB and Fastboot tools on your Android with a single command that includes all the above commands in one line.
pkg update && pkg upgrade && pkg install python && pkg install git && git clone https://github.com/freetheorange905/adb-fastboot-termux.git && cd adb-fastboot-termux && python af.py
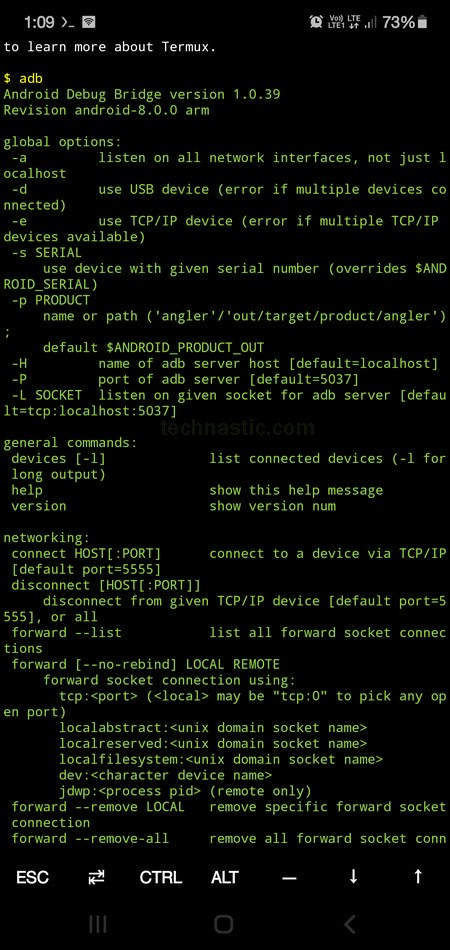
Having set up ADB and Fastboot on your device via Termux, use the following command to verify if you have done everything as expected.
adb
or
adb help
As you can see below, you’ll get information such as the Android Debug Bridge version and other ADB options on your phone’s screen.
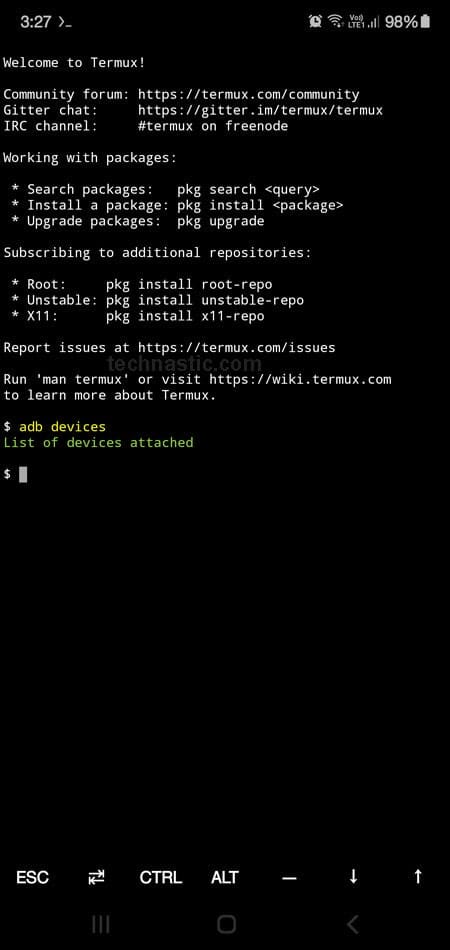
Please note that if you run the adb devices command, you won’t get any device ID under the list of devices attached because your Android device will now act like an ADB/Fastboot host.
Please note that to use ADB, your host Android device needs to be rooted, as it can be done using a Magisk module called ADB & Fastboot for Android NDK.
3. Using ADB Commands via Web ADB
Recently, a developer named Yume Chan launched a website that lets us use ADB on Android via Chrome, Opera, and Microsoft Edge browsers. It means we no longer need a rooted Android device to use ADB. WebADB makes use of the WebUSB API found in all Chromium-based desktop and mobile browsers.
WebADB lets you send ADB commands from one Android device to another, mirror the screen, and control the other device, install APKs, browse the files on the other device, capture screenshots, etc.
Prerequisites
- Two Android devices (phone or tablet).
- A USB OTG or a USB Type-C to a USB Type-C cable.
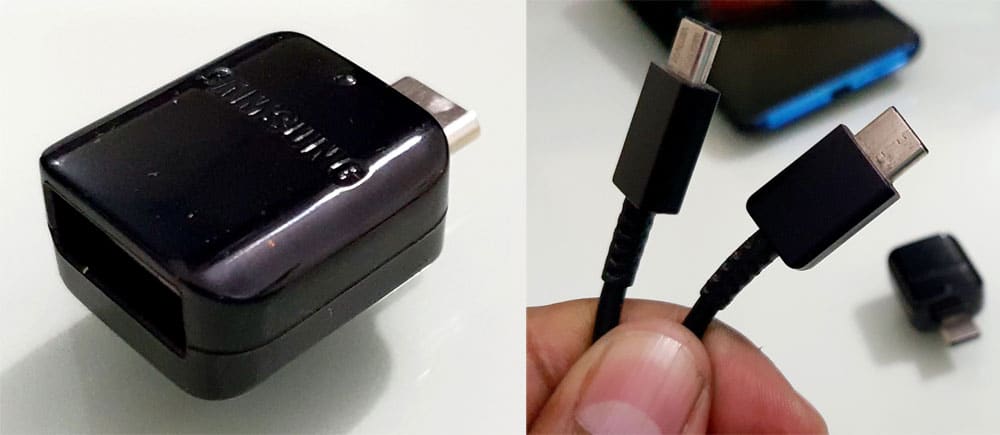

- Enable USB debugging on the Android device you want to send ADB commands.
Let’s see how to use Web ADB to run ADB commands on Android devices without root. You can use one of two Android devices as a host to perform ADB commands on the other device.
- Open the Web ADB website on the Android device you want to use as a host.
- Tap the 3-dot icon in the Chrome browser and enable the Desktop site option.
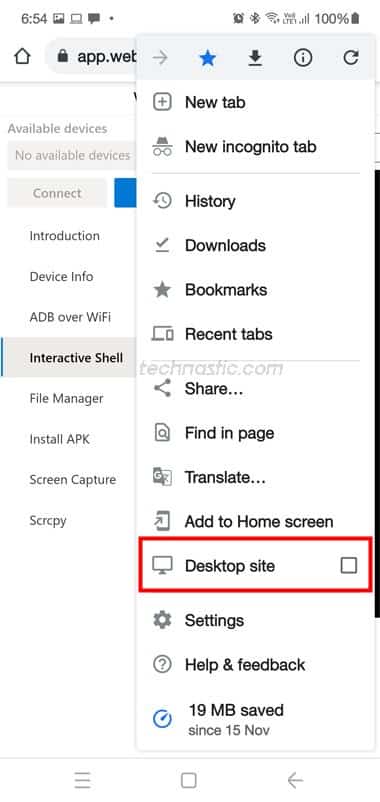
- Insert the USB OTG or the USB Type-C cable into the device you want to use as a host. Now, plug the other end of the USB cable into the client Android device you want to send the command to.
- Tap the Add Device option on the WebADB website. Select your device in the pop-up window and tap the Connect button.
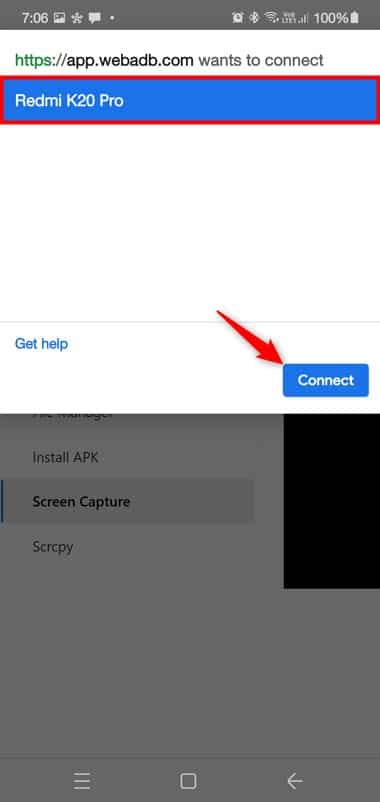
- Tap OK when the browser asks to grant access to your connected device.
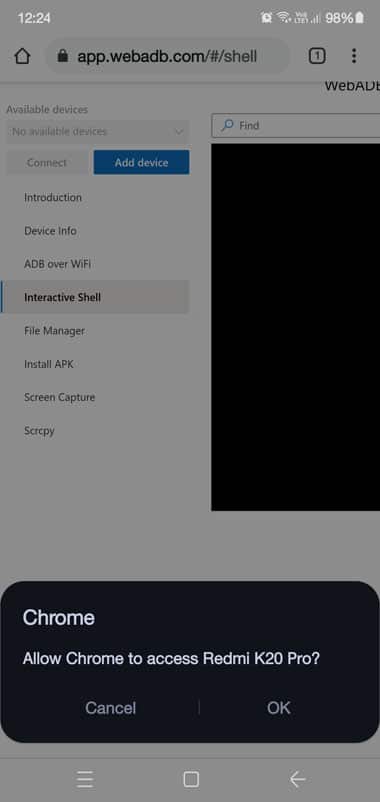
- At this point, you will receive a notification on your second device asking you to Allow USB debugging. Tap on Allow.
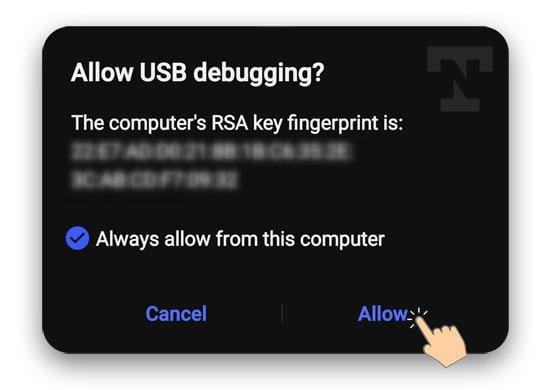
- You’ll see your device’s codename in the WebADB command box. It means that both devices have been appropriately connected for ADB operations.
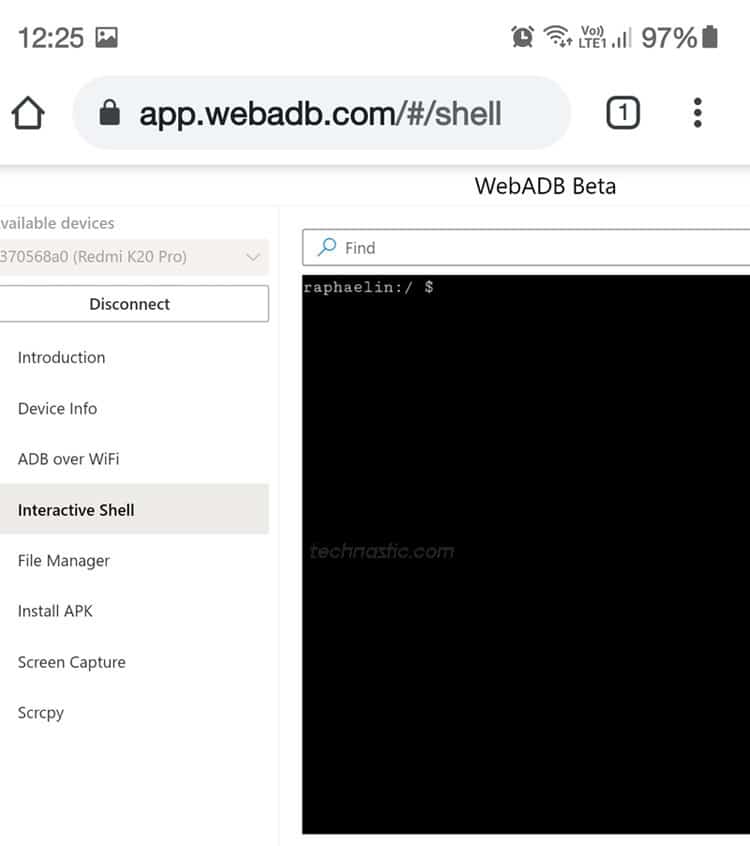
- You’re all set to use ADB commands to control the connected Android device. Don’t forget to omit “adb” and “adb shell” while executing commands on a computer. For example, if you want to reboot the connected Android phone or tablet into the bootloader mode, you should use
reboot bootloaderand tap Enter on the keyboard.
You can execute any other ADB command on your Android device without a laptop or PC, without rooting your device.